Pods
A Kubernets pod is the smallest and simplest deployable unit.
A pod represents a single instance of a running process in your cluster and can contain one or more containers that share the same network namespace and storage resources.
Run Docker's "Hello World" on Kubernetes
Docker images can run in Kubernetes as pods, the following command runs
the hello-world image from Docker's Hub in Kubernetes.
This image runs its process which outputs text to the stdout and then
exits with success code.
The --restart parameter specifies that after exiting the program should
not rerun.
The --image parameter specifies the name of the image to pull.
The -it paremeter sets two options:
i: Interactive, allows to interact withstdin.t: Thettyoption allocates a pseudo-terminal for interactive sessions.
With -it we can see the output in the terminal.
kubectl run hello-world \
--restart=Never \
--image=hello-world \
-it
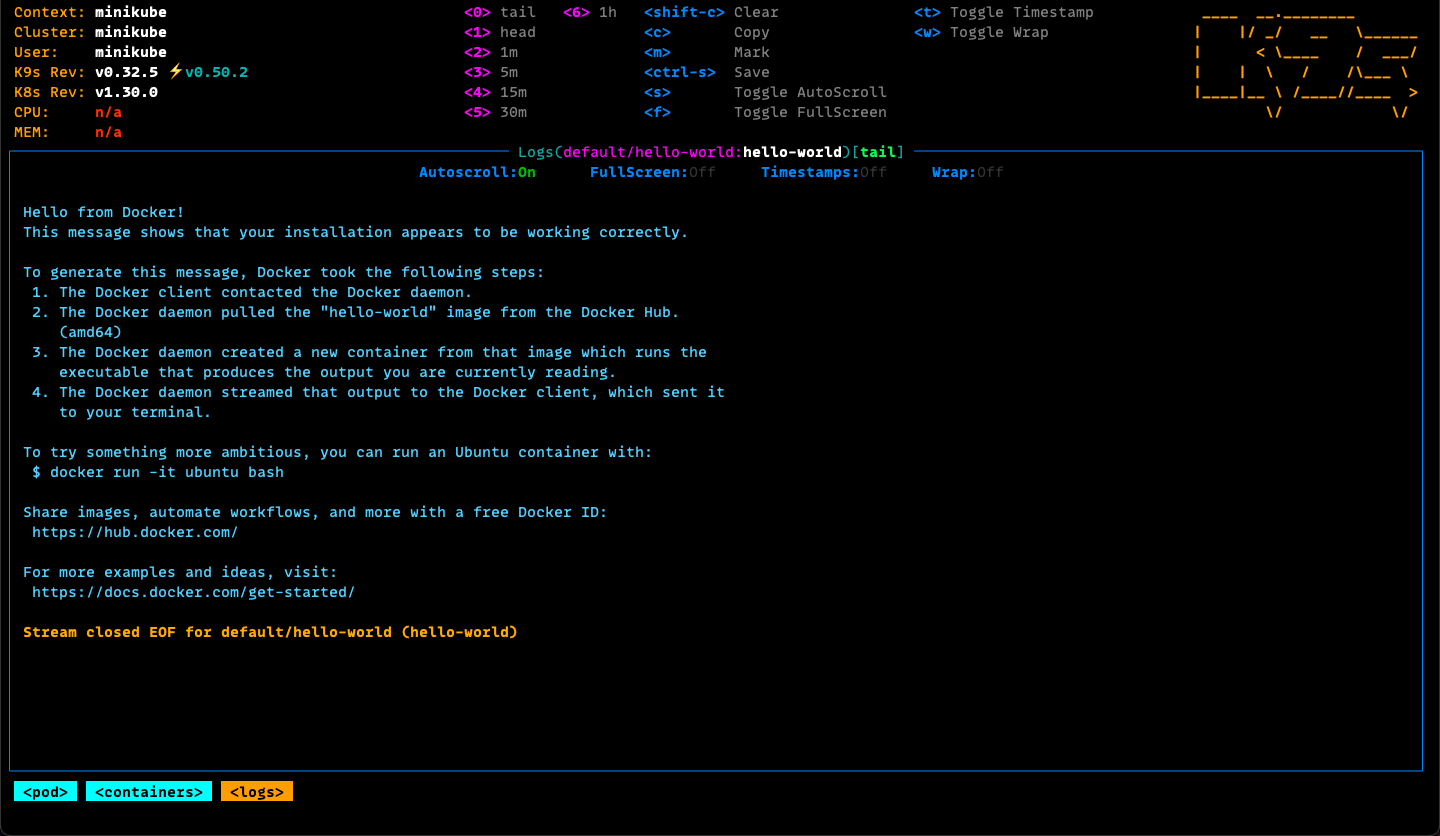
Process Logs
In regular use cases, the -it option is not likely to be used, instead
output is kept in the runtime context for the pod.
The logs subcommand can be used to check on hello-world pod logs.
kubectl logs hello-world
List Pods
kubectl get pod
The command will list every cluster pods.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-world
Inspect on Pod Details
Retrieve more details on a pod using the describe pod subcommand.
kubectl describe pod hello-world
Delete Pod
Once a pod is no longer needed, it can be deleted with pod delete subcommand.
kubectl delete pod hello-world
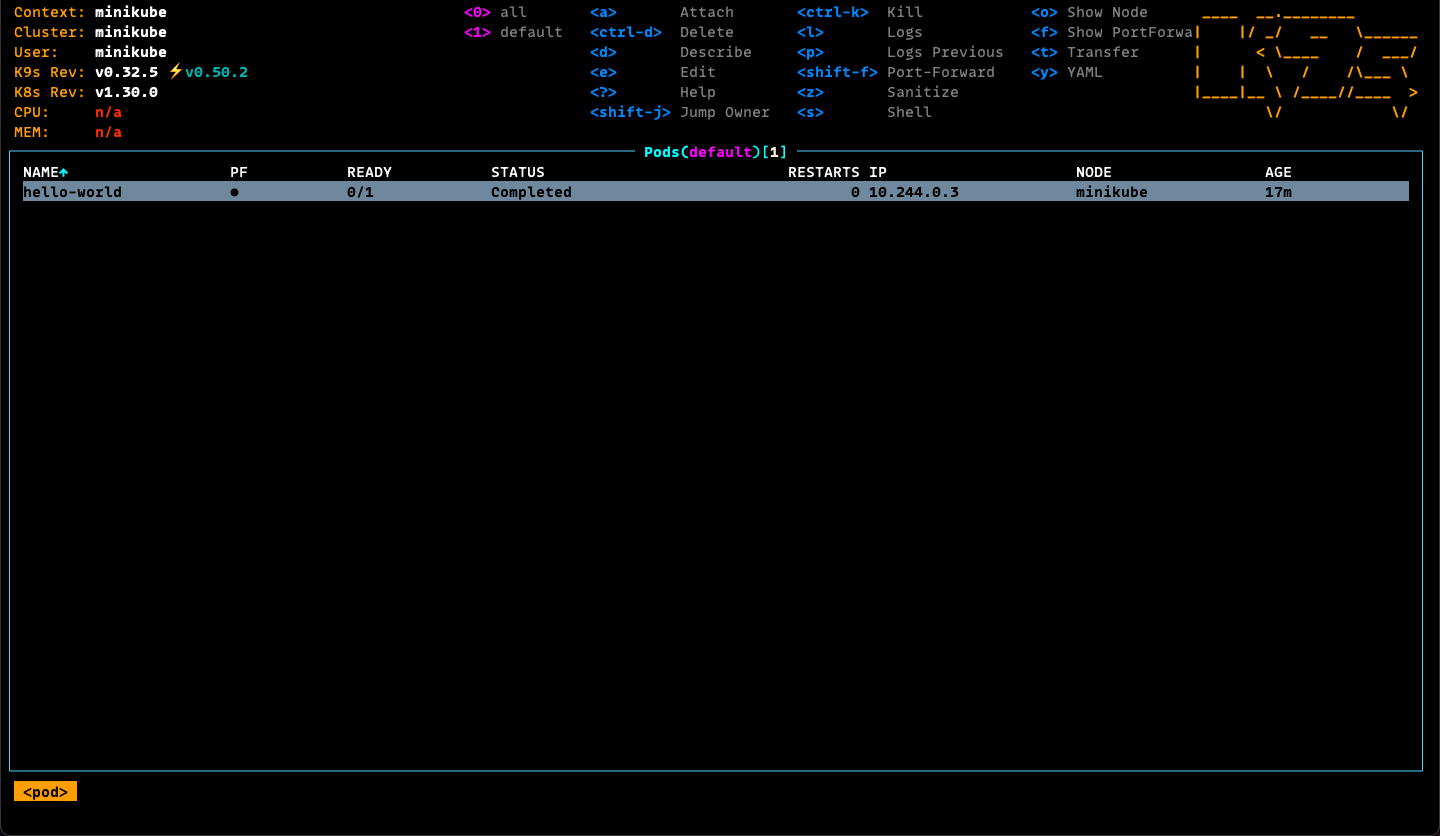
Inspect on Pod's using k9s
k9s will list Pods available in the Cluster.
Logs for the pod can be seen using the k9s interface.